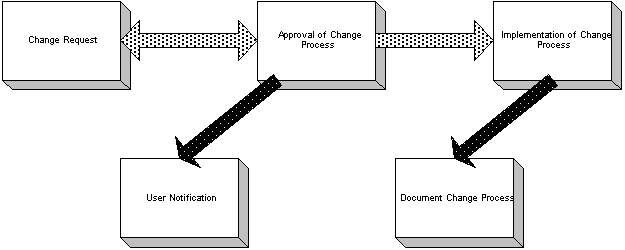
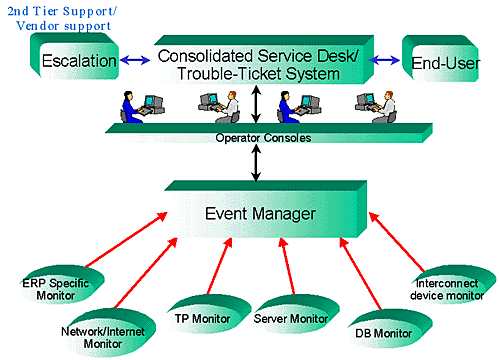
A large manufacturing company in the Northeast is utilizing its ERP system for order processing and supply chain management via an extranet to their customers and suppliers. Their Hewlett-Packard server is providing disk mirroring for the database in this three-tier client/server environment. Additionally, the database is utilizing disk striping (tablespaces were stored over several disks) to maximize performance.
One of the disks participating in the database mirroring failed, impacting the majority of the ERP system data. Order processing and portions of the inventory and financial system, were now running on virtually one disk drive. Since IT was not monitoring for this ERP component failure, the event, at first, went unnoticed -- although the disk failure was reported repeatedly to both system and database log files.
Over several days, the help desk staff noticed an increased number of calls from local users and remote customers about the performance of the ERP application, in particular, the Order Processing system. The problem got so bad that the majority of the order processing users could not get the data at all, often receiving strange error messages that indicated a network problem.
The help desk escalated the event as "network problem", but after hours of troubleshooting, the network engineer determined that the problem had to be originating from the database server.
Trying to alleviate the problem quickly, the system manager thought the best and safest course of action was to reboot the system. Unfortunately, the system failed to reboot. After hours of troubleshooting by both corporate and vendor engineers, the cause of the problem was discovered. Once the new disk arrived on site, the system was put back into production.
After rebooting, the system and database log files clearly showed that the source of the problem was disk related. If IT were monitoring these log files, the problem would have appeared immediately after the fault. A new disk could have been "hot swapped" while the system was still running in a matter of hours.
The overall problem resulted in two days of ERP system downtime. The approximate cost of downtime for this manufacturer was determined to be $50,000 per hour.